2 degree knee joint can not only reduce the patient's motor activity, but also worsen his quality of life in general. The reason for this may be not only pain and inability to exercise, which seemed insignificant until recently.
Comparing the changes that occurred between the initial stage of the disease and the second stage, a person begins to understand: without proper treatment, the condition will only worsen.
Causes of the disease
Most of the time, the reason for the transition of the disease to stage 2 is an irresponsible attitude towards treatment and non-compliance with the doctor's recommendations regarding physical activity and lifestyle changes.
In a joint already affected by disease, blood circulation and metabolic processes are slowed down to the point that tissues cannot receive nutrients and oxygen without outside help. In case of refusal of treatment or postponement of it "for later", there is an acceleration of the destructive processes in the joint and, consequently, the transformation of the disease of their mild stage to more severe.
Symptoms
Stage 2 of the knee joint is characterized by the following manifestations:
- Increased pain: pain attacks become normal (after a night's sleep, prolonged rest period, physical exercise).
- joint stiffness, usually in the morning, which disappears after a short walk.
- the knee joint increases in size, its relief is normalized - all normal flares and joint depressions are no longer identified. In the upright position, this can manifest as skin "hanging" above the knee. In a squatting position, it becomes apparent that one knee (affected by knee joints) is much larger than the other, healthy and has a spherical shape.
- when you move the knee, a characteristic crisis is heard.
- The joint bending and extension movements are abruptly limited.
People with grade 2 knee pain can rarely do without taking painkillers, as knee pain starts to bother them even during rest periods. This is due to sharp increases in the bone tissues of the joint, which irritate and injure all the structures of the knee.
How the doctor makes this diagnosis
In most cases, a patient complaining of a deteriorating health condition has already been diagnosed with knee pain and the treating physician may order an x-ray to evaluate changes in the joint.
CT, MRI and laboratory blood tests may be suggested if the doctor has reason to suspect other diseases related to knee arthroplasty. This is necessary to rule out infections that can penetrate the joint through the bloodstream and a complex knee joint, with damage to the soft tissues.Complications of the disease
In the absence of treatment or an insufficiently responsible attitude towards him, the grade 2 knee joint can quickly overcome the last "stage" and reach the final stage, in which the pain becomes a constant companion and the joints become irreversible. changes and deformations.
In addition, weakened joint tissues become vulnerable to infections and any viral or bacterial systemic disease can cause serious complications during the knee joint. The most common, but no less dangerous, is the infection of the joint cavity with the formation of purulent contents, which can spread to soft tissues - muscles, skin.Treatment
In the treatment of grade 2 knee arthritis, the focus is on relieving pain, slowing down or completely stopping the degenerative process in the joint, preventing complications and improving knee mobility.
Medicines
Drugs used to treat grade 2 knee arthritis are divided into the following groups:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs.These include the latest generation of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which eliminate the inflammatory process in the joint and, consequently, reduce pain.
- Chondroprotectors.This group of drugs helps protect cartilage tissue from further damage and enhances regenerative processes in it.
- Hyaluronic acid preparations,which are proportional to the natural lubrication of the inner surface of the joint. By reducing friction in the knee joint, these drugs prevent further cartilage damage. In some cases, intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid are indicated (for example, with very poor blood circulation in the joint, which prevents other forms of the drug from reaching the affected tissues).
- Aids.These include vitamin preparations, immunostimulants, bioactive plant extracts (aloe, echinacea, etc. ) designed to improve blood circulation to joint tissues and thus accelerate metabolic processes. .
Physiotherapy, massage, gymnastics
Such treatment methods as physiotherapy, massage therapy and exercise therapy can be considered helpful in the treatment of grade 2 knee joint and are rarely used as independent treatments.
Physiotherapy (UHF, phonophoresis, ultrasound therapy, magnetotherapy) is used to improve blood circulation to the joint and stimulate recovery processes in it.
One of the most effective physiotherapy procedures for the treatment of arthritis is MLS laser therapy with the ability to adjust the power of the laser beam. The treatment uses constant and pulsed wavelengths, due to which deep penetration into the tissues is achieved and a strong clinical result. The MLS laser treats all diseases of the joints, osteochondrosis, hernias and other diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
The massage is recommended to be done in courses of 10-15 sessions, one session daily or every other day. Massage, improving blood supply to the joint, normalizes metabolic processes in it and provides a more effective effect of drugs on the tissues affected by the disease.
In the diagnosis of 2nd degree knee joint pain, massage is often prescribed with the use of drugs (chondroprotective agents, anti-inflammatory or irritating ointments, cooling and external anesthetic agents). factors.
The complex of physiotherapy exercises is assigned to the treating physicians after evaluation of the effectiveness of the drug treatment and is selected taking into account the individual characteristics of the course of the disease and the general health of the patient.
Lifestyle correction
Lifestyle correction is one of the most important conditions for effective treatment. With a 2nd degree knee joint, you must follow these rules:
- Reduce the load on the diseased joint.For this, orthopedic rods are used, which allow you to distribute the load during the movement in such a way that the knee joint is slightly involved. It is important to choose the right cane for your height - it should be from the wrist to the floor when standing.
- Nutrition.For this disease, it is recommended to reduce the consumption of foods containing animal protein (eggs, meat, fish, whole milk), carbohydrates (baked goods, sweets) and any foods and beverages containing synthetic flavors, sweeteners, preservatives. .
- Weight loss. Obesity is one of the risk factors that increases the likelihood of metabolic disorders in all tissues, including joint tissues. In addition, being overweight is an unnecessary strain on the joints.
Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment can be divided into two types: arthroscopy and endoprosthesis.
Each function has its own list of indications for which intervention will be most effective.
Arthroscopy
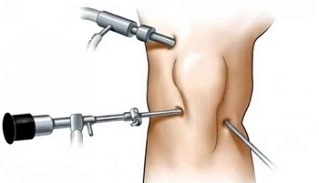
Arthroscopy is a low-trauma surgical procedure in which surgery is performed using microscopic lighting, surgical devices, and video devices inserted into the joint cavity through small centers.
Reading:
- presence of bone neoplasms (osteophytes) that impede joint mobility.
- deformities of the joint tissues, which can be corrected without large-scale surgery.
- the need for chondroplasty, which can significantly slow the progression of the disease and restore the ability of the joint to move.
Endoprosthetics
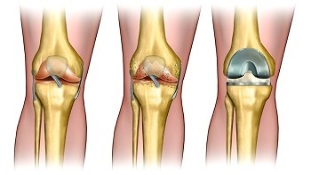
Endoprosthetics - replacement of knee joint with artificial from durable and hypoallergenic material, identical structure with natural bone tissue.
Over time, the prosthesis takes over all the functions of the "mother" joint and allows you to return to normal life.
Reading:
- no effect after a long course of conservative treatment.
- rapid progression of the disease?
- Changes in the joint significantly impair the patient's motor activity, cause severe and frequent pain and / or cause a risk of disability.
Among the absolute contraindications there are only systemic diseases that make any surgery impossible.
The treating physician weighs the risks and benefits of surgery and, based on the findings, makes a decision about the need for surgery or the continuation of a conservative treatment.

















































